Rodzaje źródeł światła (lamp)
Lampa LED Dioda emitująca światło, szerzej znana jako dioda LED. Działanie diody elektroluminescencyjnej opiera się na zjawisku rekombinacji nośników ładunku. Zjawisko to zachodzi w półprzewodnikach wówczas, gdy elektrony na powłokach elektronowych półprzewodnika, przechodzą z wyższego poziomu energetycznego na niższy, ale zachowują swój pseudo-pęd. Fizycy nazwali to przejściem prostym. Podczas tego przejścia energia elektronu zostaje zamieniona na kwant promieniowania elektromagnetycznego. Przejścia tego rodzaju dotyczą półprzewodników z prostym układem pasmowym. W takich półprzewodnikach minimum pasma przewodnictwa i wierzchołkowi pasma walnecyjnego odpowiada ta sama wartość pędu. Istnieje kilka rodzajów diód wykorzystywanych w oświetleniu: HBLED (High Brightness LED) – diody o wysokiej jasności świecenia czyli takie, których jasność przekracza 0,2 cd; stosowane są tam, gdzie zwykle używa się tradycyjnych źródeł światła – w sygnalizacji ulicznej, w latarkach, w oświetleniu pojazdów. RGB LED (Red, Green, Blue) – dioda mająca możliwość do generowania trzech podstawowych barw (czerwony, zielony, niebieski), a przez to, przez możliwość ich mieszania i tworzenia praktycznie dowolnej barwy. Power LED – Dioda LED o wysokiej mocy, do prawidłowej pracy konieczne jest zapewnienia jej właściwego chłodzenia i zasilania. Białe diody typu Power LED mają zazwyczaj emiter wielkości około 1mm2.
Lampa OLED Światło uzyskiwane jest z organicznych polimerów. Polimer umieszcza się pomiędzy dwoma elektrodami na których jest różnica potencjałów. Dzięki temu uzyskuje się przepływ prądu. Od katody do anody prąd może płynąć tylko w jednym kierunku. W kierunku przeciwnym do ruchu elektronów poruszają się dziury. Zderzenia tych cząstek wywołują emisję promieniowania świetlnego.
Lampa fluorescencyjna Lampa wyładowcza, w której światło wytwarzane jest przez wzbudzenie warstwy luminoforu przy pomocy promieniowania ultrafioletowego, wytworzonego podczas wyładowania. Nazwę tę najczęściej stosuje się w odniesieniu do niskoprężnej lampy rtęciowej. Potocznie nazywana jest także świetlówką lub jarzeniówką.
Lampa halogenowa Lampa żarowa wypełniona gazem, zawierająca włókno (skrętkę) wolframowe i małą ilość halogenków.
Lampa żarowa Lampa, w której światło wytwarzane jest poprzez podgrzanie jednego elementu (najczęściej jest to skrętka wolframowa) do momentu żarzenia. Podgrzanie jest skutkiem przepuszczenia przez skrętkę prądu elektrycznego. Lampa ta popularnie zwana jest żarówką.
Lampa indukcyjna Lampa o oznaczeniu QL działająca w oparciu o zasadę funkcjonowania niskoprężnej lampy rtęciowej, jednak bez zastosowania elektrod. Jonizacja gazu w przestrzeni wyładowczej uzyskiwana jest w procesie indukcji elektromagnetycznego pola wysokiej częstotliwości.
Lampa metalohalogenkowa Lampa wyładowcza, w której światło powstaje w wyniku promieniowania mieszaniny par metalu (np. rtęci) i produktów rozkładu halogenków (np. halogenków talu, indu albo sodu).
Lampa sodowa Lampa zawierająca pary sodu, w której ciśnienie cząstkowe par podczas pracy nie przekracza 5 Pa (niskoprężna lama sodowa) lub w której ciśnienie cząstkowe podczas pracy jest rzędu 104 Pa (wysokoprężna lampa sodowa)
Lampa rtęciowa Lampa zawierająca pary rtęci, pokryta warstwą luminoforu lub bez niej, w której ciśnienie cząstkowe par podczas pracy nie przekracza 100 Pa (niskoprężna lampa rtęciowa) lub w której ciśnienie cząstkowe podczas pracy dochodzi do 105 Pa (wysokoprężna lampa rtęciowa)
Lampa rtęciowo – żarowa Lampa zawierająca w tej samej bańce rurkę wyładowczą wysokoprężnej lampy rtęciowej oraz skrętkę lampy żarowej, połączone szeregowo.
Rodzaje trzonków
Trzonek to część lampy służąca do jej umocowania w oprawce, zwykle także do jej połączenia z obwodem zasilającym. Rodzaj trzonka i odpowiadającej mu oprawki z reguły opisywany jest jedną lub kilkoma literami oraz liczbą, wskazującą przybliżony wymiar trzonka w milimetrach (przeważnie średnicę lub rozstaw bolców). Najczęściej spotykane rodzaje trzonków:
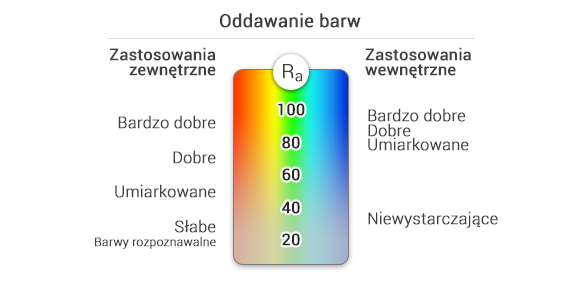
Wskaźnik oddawania barw
Aby zapewnić dobre odwzorowanie kolorów i właściwy kontrast barwy, należy stosować źródła światła o wysokim wskaźniku oddawania barw. Wówczas przedmioty, które obserwujemy prezentują się w swoich naturalnych, niezafałszowanych kolorach. Wskaźnik oddawania barw Ra posiada maksymalną wartość 100. Podaje on informację o tym, w jakim stopniu dane źródło światła umożliwia obserwację kolorów. W pomieszczeniach przeznaczonych do pracy, powinny być stosowane te źródła światła, których współczynnik oddawania barw jest większy od 80. Natomiast w tych pomieszczeniach, w których wierna prezentacja kolorów jest szczególnie istotna, np. w szkolnych salach zajęć plastycznych, w sklepach odzieżowych, w sklepach z farbami, w gabinetach stomatologicznych, wskazane jest stosowanie źródeł światła, których Ra jest większe od 90.
Temperatura barwowa
O wrażeniu kolorystycznym oglądanego otoczenia decyduje między innymi rodzaj bieli, jaki wysyłany jest ze źródła światła. Parametr ten określany jest mianem temperatury barwowej Tb. Różne źródła światła emitują światło o różnej temperaturze barwowej. Podobnie światło naturalne, które dociera do nas, w zależności od położenia słońca na nieboskłonie i stopnia zachmurzenia posiada różną barwę. Zaczynając od niebieskawego, przy całkowitym zachmurzeniu, do pomarańczowego, przy zachodzie słońca. Światło ciepłe wpływa uspokajająco i relaksująco. Przy tym właśnie świetle dobrze odpoczywamy i im cieplejsze światło, tym większe wrażenie ciepła i spokoju. Światło białe, czy też chłodno-białe jest bardziej stymulujące i daje lepsze warunki do intensywnej pracy.
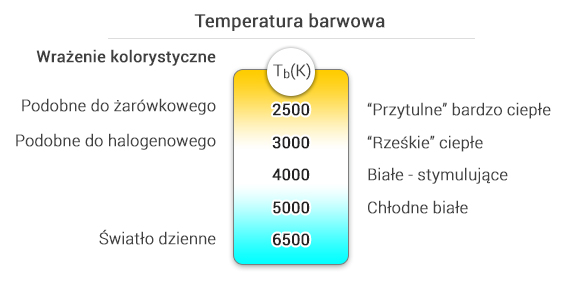
Temperatura barwowa określana jest przez porównanie barwy światła wysyłanego przez dane źródło, z odpowiadającą mu barwą ciała czarnego o określonej temperaturze. W praktyce stosuje się następujące przedziały i sformułowania przy określaniu temperatury barwowej:
<2700K Barwa żółto-biała
2700K-3500K Barwa ciepłobiała
3500K-5000K Barwa neutralna (chłodnobiała)
5000K-6500K Barwa dzienna (zimnobiała)
8000-10000K Bezchmurne niebo w południe zimą
20000K Bezchmurne niebo latem w pobliżu równika
28000-30000K Temperatura wyładowania piorunowego (błyskawicy)
Strumień świetlny
Parametr określającym całkowitą moc światła emitowanego z danego źródła (lampy). Wielkość tą wyprowadza się ze strumienia energetycznego (moc wysyłana, przenoszona lub przejmowana w postaci promieniowania tzw. moc promienista) na podstawie stopnia jego oddziaływania na oko obserwatora normalnego (odniesieniowego):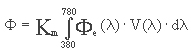
gdzie:
Φe(λ) - rozkład widmowy strumienia energetycznego,
V(λ) - skuteczność świetlna widmowa względna,
Km - skuteczność świetlna promieniowania,
λ - długość fali elektromagnetycznej.
W odniesieniu do źródeł światła, strumień świetlny oznaczany może być symbolem Φźr. Natomiast moc światła wysyłanego przez oprawę określa strumień świetlny oprawy Φopr. Dodatkowo dla opraw oświetleniowych podawany jest strumień świetlny półprzestrzeni dolnej Φˇ i półprzestrzeni górnej Φˆ. Określają one moc światła wysyłanego z oprawy odpowiednio w dół i w górę. Strumień świetlny Φ wyrażany jest w lumenach [lm].
Światłość
Światłość określa ilość światła wysyłaną w konkretnym kierunku. Przy pomocy światłości tworzy się krzywe rozsyłu oprawy oświetleniowej. Światłość I wyrażana jest w kandelach [cd]. Jest to iloraz strumienia świetlnego Φ, wysyłanego przez źródło w elementarnym kącie przestrzennym w zawierającym dany kierunek, do wartości tego elementarnego kąta.
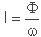
Natężenie oświetlenia
Natężenie oświetlenia jest tą ilością światła, która wysłana z oprawy dociera do powierzchni pracy. Natężenie oświetlenia E wyrażane w luksach [lx]. Jest to iloraz strumienia świetlnego Φ padającego na elementarną powierzchnię S, zawierającą dany punkt, do wartości tej elementarnej powierzchni:
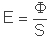
Klasa ochronności przed porażeniem elektrycznym
IP - Objaśnienia stopnia odporności na wnikanie ciał stałych, pyłu i wilgoci.
Lampa LED Dioda emitująca światło, szerzej znana jako dioda LED. Działanie diody elektroluminescencyjnej opiera się na zjawisku rekombinacji nośników ładunku. Zjawisko to zachodzi w półprzewodnikach wówczas, gdy elektrony na powłokach elektronowych półprzewodnika, przechodzą z wyższego poziomu energetycznego na niższy, ale zachowują swój pseudo-pęd. Fizycy nazwali to przejściem prostym. Podczas tego przejścia energia elektronu zostaje zamieniona na kwant promieniowania elektromagnetycznego. Przejścia tego rodzaju dotyczą półprzewodników z prostym układem pasmowym. W takich półprzewodnikach minimum pasma przewodnictwa i wierzchołkowi pasma walnecyjnego odpowiada ta sama wartość pędu. Istnieje kilka rodzajów diód wykorzystywanych w oświetleniu: HBLED (High Brightness LED) – diody o wysokiej jasności świecenia czyli takie, których jasność przekracza 0,2 cd; stosowane są tam, gdzie zwykle używa się tradycyjnych źródeł światła – w sygnalizacji ulicznej, w latarkach, w oświetleniu pojazdów. RGB LED (Red, Green, Blue) – dioda mająca możliwość do generowania trzech podstawowych barw (czerwony, zielony, niebieski), a przez to, przez możliwość ich mieszania i tworzenia praktycznie dowolnej barwy. Power LED – Dioda LED o wysokiej mocy, do prawidłowej pracy konieczne jest zapewnienia jej właściwego chłodzenia i zasilania. Białe diody typu Power LED mają zazwyczaj emiter wielkości około 1mm2.
Lampa OLED Światło uzyskiwane jest z organicznych polimerów. Polimer umieszcza się pomiędzy dwoma elektrodami na których jest różnica potencjałów. Dzięki temu uzyskuje się przepływ prądu. Od katody do anody prąd może płynąć tylko w jednym kierunku. W kierunku przeciwnym do ruchu elektronów poruszają się dziury. Zderzenia tych cząstek wywołują emisję promieniowania świetlnego.
Lampa fluorescencyjna Lampa wyładowcza, w której światło wytwarzane jest przez wzbudzenie warstwy luminoforu przy pomocy promieniowania ultrafioletowego, wytworzonego podczas wyładowania. Nazwę tę najczęściej stosuje się w odniesieniu do niskoprężnej lampy rtęciowej. Potocznie nazywana jest także świetlówką lub jarzeniówką.
Lampa halogenowa Lampa żarowa wypełniona gazem, zawierająca włókno (skrętkę) wolframowe i małą ilość halogenków.
Lampa żarowa Lampa, w której światło wytwarzane jest poprzez podgrzanie jednego elementu (najczęściej jest to skrętka wolframowa) do momentu żarzenia. Podgrzanie jest skutkiem przepuszczenia przez skrętkę prądu elektrycznego. Lampa ta popularnie zwana jest żarówką.
Lampa indukcyjna Lampa o oznaczeniu QL działająca w oparciu o zasadę funkcjonowania niskoprężnej lampy rtęciowej, jednak bez zastosowania elektrod. Jonizacja gazu w przestrzeni wyładowczej uzyskiwana jest w procesie indukcji elektromagnetycznego pola wysokiej częstotliwości.
Lampa metalohalogenkowa Lampa wyładowcza, w której światło powstaje w wyniku promieniowania mieszaniny par metalu (np. rtęci) i produktów rozkładu halogenków (np. halogenków talu, indu albo sodu).
Lampa sodowa Lampa zawierająca pary sodu, w której ciśnienie cząstkowe par podczas pracy nie przekracza 5 Pa (niskoprężna lama sodowa) lub w której ciśnienie cząstkowe podczas pracy jest rzędu 104 Pa (wysokoprężna lampa sodowa)
Lampa rtęciowa Lampa zawierająca pary rtęci, pokryta warstwą luminoforu lub bez niej, w której ciśnienie cząstkowe par podczas pracy nie przekracza 100 Pa (niskoprężna lampa rtęciowa) lub w której ciśnienie cząstkowe podczas pracy dochodzi do 105 Pa (wysokoprężna lampa rtęciowa)
Lampa rtęciowo – żarowa Lampa zawierająca w tej samej bańce rurkę wyładowczą wysokoprężnej lampy rtęciowej oraz skrętkę lampy żarowej, połączone szeregowo.
Rodzaje trzonków
Trzonek to część lampy służąca do jej umocowania w oprawce, zwykle także do jej połączenia z obwodem zasilającym. Rodzaj trzonka i odpowiadającej mu oprawki z reguły opisywany jest jedną lub kilkoma literami oraz liczbą, wskazującą przybliżony wymiar trzonka w milimetrach (przeważnie średnicę lub rozstaw bolców). Najczęściej spotykane rodzaje trzonków:
| Trzonki gwintowane | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trzonki do lamp niskonapięciowych | ||||||
| Trzonki dwubolcowe | ||||||
| Trzonki czterobolcowe | ||||||
| Trzonki do lamp dwukońcowych | ||||||
Wskaźnik oddawania barw
Aby zapewnić dobre odwzorowanie kolorów i właściwy kontrast barwy, należy stosować źródła światła o wysokim wskaźniku oddawania barw. Wówczas przedmioty, które obserwujemy prezentują się w swoich naturalnych, niezafałszowanych kolorach. Wskaźnik oddawania barw Ra posiada maksymalną wartość 100. Podaje on informację o tym, w jakim stopniu dane źródło światła umożliwia obserwację kolorów. W pomieszczeniach przeznaczonych do pracy, powinny być stosowane te źródła światła, których współczynnik oddawania barw jest większy od 80. Natomiast w tych pomieszczeniach, w których wierna prezentacja kolorów jest szczególnie istotna, np. w szkolnych salach zajęć plastycznych, w sklepach odzieżowych, w sklepach z farbami, w gabinetach stomatologicznych, wskazane jest stosowanie źródeł światła, których Ra jest większe od 90.

Temperatura barwowa
O wrażeniu kolorystycznym oglądanego otoczenia decyduje między innymi rodzaj bieli, jaki wysyłany jest ze źródła światła. Parametr ten określany jest mianem temperatury barwowej Tb. Różne źródła światła emitują światło o różnej temperaturze barwowej. Podobnie światło naturalne, które dociera do nas, w zależności od położenia słońca na nieboskłonie i stopnia zachmurzenia posiada różną barwę. Zaczynając od niebieskawego, przy całkowitym zachmurzeniu, do pomarańczowego, przy zachodzie słońca. Światło ciepłe wpływa uspokajająco i relaksująco. Przy tym właśnie świetle dobrze odpoczywamy i im cieplejsze światło, tym większe wrażenie ciepła i spokoju. Światło białe, czy też chłodno-białe jest bardziej stymulujące i daje lepsze warunki do intensywnej pracy.

Temperatura barwowa określana jest przez porównanie barwy światła wysyłanego przez dane źródło, z odpowiadającą mu barwą ciała czarnego o określonej temperaturze. W praktyce stosuje się następujące przedziały i sformułowania przy określaniu temperatury barwowej:
<2700K Barwa żółto-biała
2700K-3500K Barwa ciepłobiała
3500K-5000K Barwa neutralna (chłodnobiała)
5000K-6500K Barwa dzienna (zimnobiała)
8000-10000K Bezchmurne niebo w południe zimą
20000K Bezchmurne niebo latem w pobliżu równika
28000-30000K Temperatura wyładowania piorunowego (błyskawicy)
Strumień świetlny
Parametr określającym całkowitą moc światła emitowanego z danego źródła (lampy). Wielkość tą wyprowadza się ze strumienia energetycznego (moc wysyłana, przenoszona lub przejmowana w postaci promieniowania tzw. moc promienista) na podstawie stopnia jego oddziaływania na oko obserwatora normalnego (odniesieniowego):
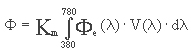
gdzie:
Φe(λ) - rozkład widmowy strumienia energetycznego,
V(λ) - skuteczność świetlna widmowa względna,
Km - skuteczność świetlna promieniowania,
λ - długość fali elektromagnetycznej.
W odniesieniu do źródeł światła, strumień świetlny oznaczany może być symbolem Φźr. Natomiast moc światła wysyłanego przez oprawę określa strumień świetlny oprawy Φopr. Dodatkowo dla opraw oświetleniowych podawany jest strumień świetlny półprzestrzeni dolnej Φˇ i półprzestrzeni górnej Φˆ. Określają one moc światła wysyłanego z oprawy odpowiednio w dół i w górę. Strumień świetlny Φ wyrażany jest w lumenach [lm].
Światłość
Światłość określa ilość światła wysyłaną w konkretnym kierunku. Przy pomocy światłości tworzy się krzywe rozsyłu oprawy oświetleniowej. Światłość I wyrażana jest w kandelach [cd]. Jest to iloraz strumienia świetlnego Φ, wysyłanego przez źródło w elementarnym kącie przestrzennym w zawierającym dany kierunek, do wartości tego elementarnego kąta.
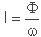
Natężenie oświetlenia
Natężenie oświetlenia jest tą ilością światła, która wysłana z oprawy dociera do powierzchni pracy. Natężenie oświetlenia E wyrażane w luksach [lx]. Jest to iloraz strumienia świetlnego Φ padającego na elementarną powierzchnię S, zawierającą dany punkt, do wartości tej elementarnej powierzchni:
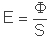
Klasa ochronności przed porażeniem elektrycznym
Brak symbolu |
Klasa bezpieczeństwa 0 |
| Ochronę przed porażeniem elektrycznym stanowi izolacja podstawowa. W przypadku uszkodzenia izolacji ochronę przeciwporażeniową powinny zapewnić odpowiednio korzystne warunki środowiskowe oraz położenie urządzenia poza dotykiem bezpośrednim. |
Klasa bezpieczeństwa I |
|
| W urządzeniach z I klasą ochronności bezpieczeństwo zapewnione jest poprzez połączenie wszystkich czynnych przewodzących elementów z przewodem ochronnym lub bezpośrednio z uziemieniem. |
Klasa bezpieczeństwa II |
|
| W urządzeniach z II klasą ochronności bezpieczeństwo zapewnione jest przez zastosowanie izolacji podwójnej lub wzmocnionej, której w danych warunkach środowiskowych i przy napięciu znamionowym uważa się za nie do przebicia. |
Klasa bezpieczeństwa III |
|
| Ochrona przeciwporażeniowa w urządzeniach III klasy ochronności jest zapewniona przez obniżenie napięcia zasilania do wartości bezpiecznej w danych warunkach środowiskowych. |
IP - Objaśnienia stopnia odporności na wnikanie ciał stałych, pyłu i wilgoci.
| I | Stopień zabezpieczenia przed nieumyślnym kontaktem z częściami pod napięciem |
P | Stopień zabezpieczenia przed wilgocią |
| 0 | Brak ochrony Brak specjalnych środków ochrony. | 0 | Brak ochrony Brak specjalnych środków ochrony. |
| 1 | Ochrona przed ciałami stałymi o wielkości ponad 50mm. Duża powierzchnia ciała ludzkiego, równa np. powierzchni dłoni (brak zabezpieczenia przed dotykiem). Ciała stałe o średnicy ponad 50mm. | 1 | Ochrona przed pionowo wpadającymi kroplami wody. Padające pionowo krople wody nie mogą wywołać szkodliwych skutków w urządzeniu. |
| 2 | Ochrona przed ciałami stałymi przekraczającymi 12mm. Palec lub podobne przedmioty o długości nie przekraczającej 80mm. Ciała stałe o średnicy nie przekraczającej 12mm. | 2 | Ochrona przed kroplami wody przy przechyleniu do 15°. Padające pionowo krople wody nie mogą wywołać szkodliwych skutków przy przechyle osłony urządzenia do 15° względem położenia normalnego. |
| 3 | Ochrona przed ciałami stałymi przekraczającymi 2,5mm. Narzędzia, drut, itp. o średnicy lub grubości przekraczającej 2,5mm. Ciała stałe o średnicy powyżej 2,5mm. | 3 | Ochrona przed rozpyloną wodą. Rozpylona woda padająca pod kątem 60° od pionu nie powinna wywołać szkodliwych efektów. |
| 4 | Ochrona przed ciałami stałymi przekraczającymi 1mm. Drut lub taśma o grubości 1 mm Ciała stałe o średnicy 1mm. | 4 | Ochrona przed bryzgami wody. Woda rozbryzgiwana na osłonę z dowolnego kierunku nie powinna wywołać szkodliwych skutków. |
| 5 | Pyłoodporność. Niewielka ilość pyłu przedostaje się do wnętrza osłony, lecz jest tak mała, że nie wywiera ujemnego wpływu na pracę wyposażenia. | 5 | Ochrona przed strugami wody. Woda z dyszy skierowana na obudowę z dowolnego kierunku nie powinna wywołać szkodliwych skutków. |
| 6 | Pyłoszczelność. Pył nie przedostaje się do wnętrza osłony. | 6 | Ochrona przed falami. Woda po zalaniu falą lub od silnej strugi nie może dostać się do wnętrza osłony w takiej ilości, aby wywołać szkodliwe skutki. |
| 7 | Ochrona przed zanurzeniem. Przy zanurzeniu urządzenia do wody na określony czas i przy określonym ciśnieniu, woda nie może dostać się do wnętrza osłony w takiej ilości, aby wywołać szkodliwe skutki. | ||
| 8 | Ochrona przed głębokim zanurzeniem. Urządzenie dostosowane do długotrwałego zanurzenia w wodzie w warunkach określonych przez wytwórcę. |
 www.struhm.com
www.struhm.com






